W
What is the « DIM ELICIT » ?
The DIM ELICIT (« Empowering LIfe sCiences with Innovative Technologies ») is the network of innovative technologies for biology in Ile-de-France region.
Co-leaded by the Institut Pierre Gilles de Gennes for microfluidics (IPGG) and the Institut Pasteur, the DIM ELICIT has been labeled “Domain Of Main Interest” by the regional council of Ile-de-France for the period 2017-2020.
Through calls for proposals, this programme supports Paris region research teams to design breakthrough technologies or to disseminate them for first applications in biology. It stimulates interdisciplinary collaborations between technologists and biologists, as well as partnerships with industries.
These technological innovations must have a strong societal impact, particularly in the biomedical field, and generate scientific and economic value in the medium term.
In order to be one of the most innovative ecosystems in the field of Technologies for Life Sciences, the DIM ELICIT ambitions to bring together research teams from all over the Ile-de-France region into one unique network.
The DIM ELICIT covers 3 core technologies, divided into 4 end-user applications.
C
Core technologies of the DIM ELICIT
Microfluidics
Microfluidics is the science of flow and fluid handling at the micrometer scale. Nature has mastered for millions of years: the sap that rises from the roots to the leaves of the tree, or the blood that circulates in our capillaries are good examples.
It is a recent field of research which is now essential in many areas of biology, particularly in medicine: to reproduce the structure and functioning of human organs, such as the kidney or the intestine, to make diagnoses or to study cancers…
It uses several types of technologies: micro-droplets, labs-on-chips, micro-actuators, 3D printing, surface patterning, low-cost technologies (such as microfluidic paper), submicrometric microfluidics, nanofluidics…
La microfluidique appliquée à la biologie | Thématique (Vidéo in french)
Biophotonics and waves
This fusion of optics and biology has given rise to a major scientific field: biophotonics. Optical technologies using the properties of light waves in microscopy have made it possible to observe, analyse or manipulate living matter with ever greater precision.
The techniques that fall under the heading of “biophotonics and waves” use the properties of light, acoustic or electromagnetic waves in order to observe, analyze or manipulate living matter.
Among these techniques are: super-resolution microscopy, associated sensor technologies, multiphoton microscopy, visible/terahertz/Raman spectroscopy, innovative probes (nanoparticles, nanosensors, etc.), optogenetics, adaptive optics, photoablation and photostimulation, positron emission tomography, etc.
Biophotonique et ondes | Thématique (Vidéo in french)
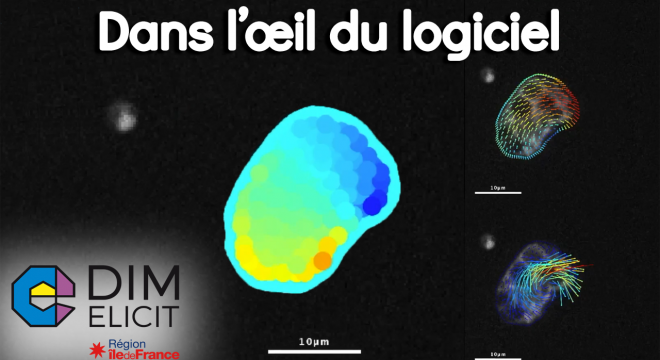
Image analysis
Biological images contain a great deal of data that may escape the human eye. Computer-assisted image analysis has radically changed the methods of measurement and study of living things.
Computer-assisted biological image analysis can process data that are not visible to the human eye, such as the perimeter, volume, or elasticity of cells observed through imaging techniques. The development of biological image analysis has thus radically changed the methods of measurement and study of living organisms. Compressive sensing, tracking, localization, digital pathology, statistical analysis, spatial analysis, harmonic analysis, optimization, automation, deep learning, software deployment in the cloud, augmented and immersive visualization, etc. are all techniques used for image analysis.
Analyse d’images biologiques | Thématique (Vidéo in french)


 fr
fr